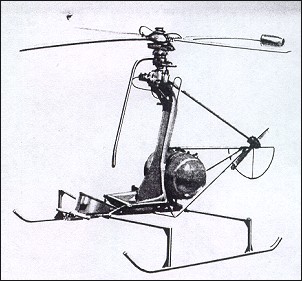
The fiberglass cabin enclosure could be dismantled in a few minutes, and underneath was a tricycle three-wheel undercarriage. The rotor head was machined from aluminum and is of the rigid rotor type. However, the larger the augmenter duct, the more drag it will produce, and it may only be effective at certain speed ranges. Karavodin, who completed a working model in 1907. He wanted a two-seater that was simple, low-cost, ultralight, and easy to fly and maintain. A collective pitch stick for vertical ascent and descent was so designed and located as to control the helicopter directionally through movement in a horizontal plane. Two years later, his company had developed and flown the first jet torque-compensating helicopter, the J-5. Five HJ-1 Hornets were manufactured: two for the Army, and three for the Navy. Its range with two passengers was close to 50 miles (80 kilometers). Inside were standard cyclic sticks and pedals to control the small tail rotor.
An easy way to remember which is which is to repeat to yourself turbines turn, and jets jet. He was already thinking of using the technology on a larger scale, dreaming of a future when large heavy-lift flying cranes, and passenger carrying sky buses would fly using tip-powered jets. Instead, this copter had, on the ends of the rotors, what looked like small buzz bomb motors and, in back of the two seats, on the small frame, there were three five-gallon propane cylinders. (240 kg), with the gross weight now 1,080 lb. Steam power to fire the piston was generated by the violent exothermic chemical reaction created when hydrogen peroxide and potassium permanganate (termed T-Stoff and Z-Stoff) are combined. It has been viewed 266 times. A 25-lb. Your email address will not be published. The department is a member of the FDLP Content Partnerships Program and an Affiliated Archive of the National Archives. The helicopter was reportedly very stable due to the proven Hiller Rotor-Matic paddles and the aircrafts high-inertia rotor. report UNT Libraries Government Documents Department, National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics. In 1909, Georges Marconnet developed the first pulsating combustor without valves.
jet rc engine planes radio drone control pulsejet aircraft engines pulse The military had requested the changes to make the aircrafts controls common with other helicopters in its fleet. While the thrust-to-weight ratio is excellent, thrust specific fuel consumption is generally very poor. Remember, as with Wikipedia, it only takes a few dollars once from every person who visits to cover our running costs. All told, Hiller manufactured 25 Hornets, and about half have survived, on display in museums across the U.S. and in private collections. The ramjet engine was also updated with a larger diameter, and new weight of 12.7 lb. Ignition in the As 014 was provided by a single automotive spark plug, mounted approximately 75cm (30in) behind the front-mounted valve array. This selection of materials from the Technical Report Archive and Image Library (TRAIL) includes hard-to-find reports published by various government agencies. This website is 100% self funded, and has been since 2006. Add to cart to save with this special offer. Each unit developed 31 lb. An extensive test and development programme is in mind for them. The radical designs, however, caution is thrown to the winds in the quest to prove an idea, and looks be dammed. Starting with ignition within the combustion chamber, a high pressure is raised by the combustion of the fuel-air mixture. The technical publications contain reports, images, and technical descriptions of research performed for U.S. government agencies. UNT Digital Library,
Hillers engineers evaluated turbojet, pulsejet, and ramjet engines, and tested them extensively on a whirl stand and a static test stand. While some valveless engines are known for being extremely fuel-hungry, other designs use significantly less fuel than a valved pulsejet, and a properly designed system with advanced components and techniques can rival or exceed the fuel efficiency of small turbojet engines. Radin, Edward J. The French inventor Georges Marconnet patented his valveless pulsejet engine in 1908, which many commentators argue[attribution needed] greatly influenced the V-1 flying bomb through engineer Paul Schmidt, who pioneered a more efficient design based on modification of the intake valves (or flaps), earning him government support from the German Air Ministry in 1933. The cycle frequency is primarily dependent on the length of the engine. However, because there is no fly-wheel effect with a pulse jet, any minor interruption of the fuel flow can cause a flame-out. University of North Texas Libraries, UNT Digital Library, National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics Collection, 25 The helicopter was once a very radical design too. Even with the end of the Hornet program, Hiller had not given up on the promise of tip-jet propulsion. In 1934, Georg Madelung and Munich-based independent designer and inventor Paul Schmidt proposed to the German Air Ministry a "flying bomb" powered by Schmidt's pulse jet. The ramjets, which have no moving parts, are constructed from heat-resisting steel, and they are attached to the blade tips by two bolts and a steel support. Pulsejet engines can be made with few[1] or no moving parts,[2][3][4] and are capable of running statically. The second type of pulsejet is known as the valveless pulsejet. This causes atomized fuel at the rear of the combustion chamber to "flash" as it comes in contact with the hot gases of the preceding column of gasthis resulting flash "slams" the reed-valves shut or in the case of valveless designs, stops the flow of fuel until a vacuum is formed and the cycle repeats. Seller assumes all responsibility for this listing. The three propane cylinders feed into a control manifold and an All valve which controls the flow of liquid propane to the motors. This used a fan blower, placed underneath the engine, which could be directed to counter torque. With commercial certification on hold, Hiller gauged the militarys interest in the Hornet. Most experienced modelers are familiar with another famous pulse jet the Dynajet which holds many speed records for model aircraft. Pulsejet fuel efficiency is a topic for hot debate, as efficiency is a relative term. One company, Beck Technologies, has produced a valved pulsejet design with variable intake geometry, allowing the intake to open and close to control ram airflow, and letting the engine produce full power at any speed. The valveless pulsejet was experimented with by the French propulsion research group SNECMA (Socit Nationale d'tude et de Construction de Moteurs d'Aviation ), in the late 1940s. The simplicity of the new Hiller-Hornet was described in a 1951 special edition of the Hiller Copter-News. Pulsejet engines are characterized by simplicity, low cost of construction, and high noise levels. start to build-up rapidly. The ceiling at full gross load was 12,000 feet (3,650 meters). Hiller decided to give up on marketing the Hornet commercially after the CAA did not approve civil certification. Hiller had long been fascinated by the idea of finding new ways to perform vertical flight that eliminated the need for a tail rotor.
plane debunked smokers metabunk experimenter eaa mystery articles Evaluations by the U.S. military would also prove the claims of lower cost and maintenance for this type of helicopter. At the operational rotor speed of 500 r.p.m. They can achieve higher top speeds, with some advanced designs being capable of operating at Mach .7 or possibly higher. All production of Hillers helicopters was focused on the military. For a small model-type engine the frequency may be around 250 pulses per second, whereas for a larger engine such as the one used on the German V-1 flying bomb, the frequency was closer to 45 pulses per second. The rotor may be hand-cranked, or turned by a portable electric motor with battery, or rotated by a small two-stroke petrol engine (described as of the motor-mower type but better explained, perhaps, as an inboard outboard built into the aircraft. He built and flew the first coaxial helicopter (the XH-44) in the U.S. in 1944, when he was just 19. Autorotation on a Hornet kept the experienced pilot honest. colspan="2" style="text-align: center; font-size: large; padding-bottom: 0.3em;" | The CAA approved the new engine in October 1954 for commercial production and sale. This concept had been considered as early as 1945. Something went wrong. Among his many achievements was the development and creation of the ramjet-powered Hiller HJ-1/YH-32 Hornet. Fuel, as a gas or liquid vapour, is either mixed with the air in the intake or directly injected into the combustion chamber. As it was developed, the helicopter took on its own form of convention: Two rotors, a main lifting rotor and a tail anti-torque rotor, grew to be the norm. When Mike was asked by several bystanders if he were actually going to fly his ram-jet copter, Mike smiled and said, Yes eventually Well, Mike, we wish you the best of luck. This one is concerned with up and down flight or, if moved from side to side, operates the rudder to control the heading of the aircraft. It turns out that Mike purchased the plans for the craft from B.W. Eight years earlier, in the midst of the Second World War, Austrian engineer Friedrich von Doblhoff built and flew his WNF 342, which sent compressed air and fuel inside the rotor blades to combustion chambers on the blade tips for propulsion. The front of the cabin comprises two very large Plexiglas panels and their frames. Really neat piece of equipment and you can easily see how much simpler the total design was compared to other helicopter designs. [9] Technically the term for this engine is the acoustic-type pulsejet, or aerodynamically valved pulsejet. The second unit is a pressure jet which is usually propelled by fuel under pressure. Descriptive information to help identify this report. The pulse detonation engine (PDE) marks a new approach towards non-continuous jet engines and promises higher fuel efficiency compared to turbofan jet engines, at least at very high speeds. The improved updated HJ-1 Hornet was designated the H-32 for the Army, and HOE-1 for the Navy. The range dropped to only 28 miles (45 kilometers), while the endurance was reduced to about 30 minutes. The present international situation, however, has dictated that the resources of the Hiller factory be devoted entirely to Service production of the type 360. When the air-fuel is ignited, these valves slam shut which means that the hot gases can only leave through the engine's tailpipe, thus creating forward thrust. Over time, the military decided that the aircrafts short range, high fuel consumption, its potential for fuel starvation, and concerns with its autorotation capabilities would not meet the acceptance standards for both the Army and Navy. Mike reported that the motors are rated at 20 pounds of static thrust, and really spin the rotor up. |-. Will it fly? Other potential industry uses were for aerial photography, publicity, courier service, and for executive transportation. Civil Aeronautics Authority (CAA) commercial certification was underway by early 1951, with commercial marketing of the Hornet planned for the spring of 1951. The small tail rotor helped to improve yaw control in the performance of the H-32. Because pulsejets are an efficient and simple way to convert fuel into heat, experimenters are using them for new industrial applications such as biomass fuel conversion, boiler and heater systems, and other applications. By this time, the rotors are already spinning at a good rate, and the noise, as Mike admits, is a low roar similar to that put out by a roofers tar pot heating up. It consists of a two-seat enclosed cabin and a tail boom, both constructed from tubular steel and covered with plastic material. Most PDE research programs use pulsejet engines for testing ideas early in the design phase. This pressure is less than the inlet pressure (upstream of the one-way valve), and so the induction phase of the cycle begins.
trzmiel jk helicopter pzl swidnik jet rotorcraft powered By properly 'tuning' the system (by designing the engine dimensions properly), a resonating combustion process can be achieved. The empty weight of the H-32 increased to 530 lb. It is by no means fantastic to foresee helicopter despatch-riders with machines rugged and simple enough to be maintained in an M.T. (110 km/h) with a top speed of 80 m.p.h. Schmidt's prototype bomb failed to meet German Air Ministry specifications, especially owing to poor accuracy, range and high cost. If youve been to any EAA Fly-In lately, youve undoubtedly seen many examples of Burt Rutans once-revolutionary designs, so you know this is true. With Schmidt now working for Argus, the pulsejet was perfected and was officially known by its RLM designation as the Argus As 109-014. Your email address will not be published.

The first working pulsejet was patented in 1906 by Russian engineer V.V. The daisy valve is less effective than a rectangular valve grid, although it is easier to construct on a small scale. Incidental advantages claimed for the Hornets ramjet power source are best listed as negatives: no carburetor to ice up; no ignition system to fail or require maintenance; no radio interference; no warming-up delays; and practically no general maintenance. Designers of modern cruise missiles do not choose pulsejet engines for propulsion, preferring turbojets or rocket engines. [6] Pulsejets have also been used in both control-line and radio-controlled model aircraft. General Henry Harley "Hap" Arnold of the United States Army Air Forces was concerned that this weapon could be built of steel and wood, in 2000 man hours and approximate cost of US$600 (in 1943).[5]. Ram jets are very fuel hungry. Hiller was not impressed with the reduced performance caused by the militarys changes. The Army followed up with another order for 12 H-32s, for a total of 14. Either a fuel pump or propane is usually used. That flight was piloted by Hiller chief test pilot Frank Peterson, but test pilot Bruce Jones did most of the experimental flight testing on the aircraft. One notable line of research of pulsejet engines includes the pulse detonation engine which involves repeated detonations in the engine, and which can potentially give high compression and good efficiency. The valves prevent the explosive gas of the ignited fuel mixture in the combustion chamber from exiting and disrupting the intake airflow, although with all practical valved pulsejets there is some 'blowback' while running statically and at low speed as the valves cannot close fast enough to stop all the gas from exiting the intake. With no torque to counter due to the lack of a traditional engine and transmission system that would normally generate it, there was no need for a tail rotor. We appreciate your consideration in this matter. In addition to the control levers the cabin contains a wobble pump, a starting button, a fuel-flow gauge, a rotor r.p.m. The small, utility two-place helicopter weighed 356 lb. The basic hovering characteristics of the rotor and propulsive characteristics of the pulse-jet engine were obtained at a range of engine speeds with the engines rigidly fixed to the blade tips and with the engines free to pivot. The National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) was a U.S. federal agency founded on March 3, 1915 to undertake, promote, and institutionalize aeronautical research. The two-bladed all-metal rotor system attached to a teetering type rotor hub. The U.S. Army and U.S. Navy ordered an evaluation quantity of the two-place upgraded Hornet in June 1952. This limits the maximum (pre-combustion) pressure ratio, to perhaps 1.2 to 1.

When the induction phase is under way, fuel in atomized form is injected into the combustion chamber to fill the vacuum formed by the departing of the previous fireball; the atomized fuel tries to fill up the entire tube including the tailpipe. The high noise levels usually make them impractical for other than military and other similarly restricted applications. Pulsejet engines, being cheap and easy to construct, were the obvious choice for the V-1's designers, given the Germans' materials shortages and overstretched industry at that stage of the war. Three YH-32A helicopters were manufactured and evaluated at the Fort Rucker Army facility in Alabama during 1957. The last of these jets is the ram jet which gets its power from gasses being introduced into the combustion chamber while the ram jet is in motion, thus the name. Getting going in the Hornet was quite simple. The H-32 became the Armys first operational ramjet helicopter, and the HOE-1 was the Navys first tip-powered jet helicopter. [6] However, pulsejets are used on a large scale as industrial drying systems, and there has been a new surge to study and apply these engines to applications such as high-output heating, biomass conversion, and alternative energy systems, as pulsejets can run on almost anything that burns, including particulate fuels such as sawdust or coal powder. The company soon had three prototypes flying: the original streamlined fiberglass-enclosed two-seater, and two stripped-down utility versions. piston engine, but that when the machine is hovering it is somewhat louder.
 An easy way to remember which is which is to repeat to yourself turbines turn, and jets jet. He was already thinking of using the technology on a larger scale, dreaming of a future when large heavy-lift flying cranes, and passenger carrying sky buses would fly using tip-powered jets. Instead, this copter had, on the ends of the rotors, what looked like small buzz bomb motors and, in back of the two seats, on the small frame, there were three five-gallon propane cylinders. (240 kg), with the gross weight now 1,080 lb. Steam power to fire the piston was generated by the violent exothermic chemical reaction created when hydrogen peroxide and potassium permanganate (termed T-Stoff and Z-Stoff) are combined. It has been viewed 266 times. A 25-lb. Your email address will not be published. The department is a member of the FDLP Content Partnerships Program and an Affiliated Archive of the National Archives. The helicopter was reportedly very stable due to the proven Hiller Rotor-Matic paddles and the aircrafts high-inertia rotor. report UNT Libraries Government Documents Department, National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics. In 1909, Georges Marconnet developed the first pulsating combustor without valves. jet rc engine planes radio drone control pulsejet aircraft engines pulse The military had requested the changes to make the aircrafts controls common with other helicopters in its fleet. While the thrust-to-weight ratio is excellent, thrust specific fuel consumption is generally very poor. Remember, as with Wikipedia, it only takes a few dollars once from every person who visits to cover our running costs. All told, Hiller manufactured 25 Hornets, and about half have survived, on display in museums across the U.S. and in private collections. The ramjet engine was also updated with a larger diameter, and new weight of 12.7 lb. Ignition in the As 014 was provided by a single automotive spark plug, mounted approximately 75cm (30in) behind the front-mounted valve array. This selection of materials from the Technical Report Archive and Image Library (TRAIL) includes hard-to-find reports published by various government agencies. This website is 100% self funded, and has been since 2006. Add to cart to save with this special offer. Each unit developed 31 lb. An extensive test and development programme is in mind for them. The radical designs, however, caution is thrown to the winds in the quest to prove an idea, and looks be dammed. Starting with ignition within the combustion chamber, a high pressure is raised by the combustion of the fuel-air mixture. The technical publications contain reports, images, and technical descriptions of research performed for U.S. government agencies. UNT Digital Library, Hillers engineers evaluated turbojet, pulsejet, and ramjet engines, and tested them extensively on a whirl stand and a static test stand. While some valveless engines are known for being extremely fuel-hungry, other designs use significantly less fuel than a valved pulsejet, and a properly designed system with advanced components and techniques can rival or exceed the fuel efficiency of small turbojet engines. Radin, Edward J. The French inventor Georges Marconnet patented his valveless pulsejet engine in 1908, which many commentators argue[attribution needed] greatly influenced the V-1 flying bomb through engineer Paul Schmidt, who pioneered a more efficient design based on modification of the intake valves (or flaps), earning him government support from the German Air Ministry in 1933. The cycle frequency is primarily dependent on the length of the engine. However, because there is no fly-wheel effect with a pulse jet, any minor interruption of the fuel flow can cause a flame-out. University of North Texas Libraries, UNT Digital Library, National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics Collection, 25 The helicopter was once a very radical design too. Even with the end of the Hornet program, Hiller had not given up on the promise of tip-jet propulsion. In 1934, Georg Madelung and Munich-based independent designer and inventor Paul Schmidt proposed to the German Air Ministry a "flying bomb" powered by Schmidt's pulse jet. The ramjets, which have no moving parts, are constructed from heat-resisting steel, and they are attached to the blade tips by two bolts and a steel support. Pulsejet engines can be made with few[1] or no moving parts,[2][3][4] and are capable of running statically. The second type of pulsejet is known as the valveless pulsejet. This causes atomized fuel at the rear of the combustion chamber to "flash" as it comes in contact with the hot gases of the preceding column of gasthis resulting flash "slams" the reed-valves shut or in the case of valveless designs, stops the flow of fuel until a vacuum is formed and the cycle repeats. Seller assumes all responsibility for this listing. The three propane cylinders feed into a control manifold and an All valve which controls the flow of liquid propane to the motors. This used a fan blower, placed underneath the engine, which could be directed to counter torque. With commercial certification on hold, Hiller gauged the militarys interest in the Hornet. Most experienced modelers are familiar with another famous pulse jet the Dynajet which holds many speed records for model aircraft. Pulsejet fuel efficiency is a topic for hot debate, as efficiency is a relative term. One company, Beck Technologies, has produced a valved pulsejet design with variable intake geometry, allowing the intake to open and close to control ram airflow, and letting the engine produce full power at any speed. The valveless pulsejet was experimented with by the French propulsion research group SNECMA (Socit Nationale d'tude et de Construction de Moteurs d'Aviation ), in the late 1940s. The simplicity of the new Hiller-Hornet was described in a 1951 special edition of the Hiller Copter-News. Pulsejet engines are characterized by simplicity, low cost of construction, and high noise levels. start to build-up rapidly. The ceiling at full gross load was 12,000 feet (3,650 meters). Hiller decided to give up on marketing the Hornet commercially after the CAA did not approve civil certification. Hiller had long been fascinated by the idea of finding new ways to perform vertical flight that eliminated the need for a tail rotor. plane debunked smokers metabunk experimenter eaa mystery articles Evaluations by the U.S. military would also prove the claims of lower cost and maintenance for this type of helicopter. At the operational rotor speed of 500 r.p.m. They can achieve higher top speeds, with some advanced designs being capable of operating at Mach .7 or possibly higher. All production of Hillers helicopters was focused on the military. For a small model-type engine the frequency may be around 250 pulses per second, whereas for a larger engine such as the one used on the German V-1 flying bomb, the frequency was closer to 45 pulses per second. The rotor may be hand-cranked, or turned by a portable electric motor with battery, or rotated by a small two-stroke petrol engine (described as of the motor-mower type but better explained, perhaps, as an inboard outboard built into the aircraft. He built and flew the first coaxial helicopter (the XH-44) in the U.S. in 1944, when he was just 19. Autorotation on a Hornet kept the experienced pilot honest. colspan="2" style="text-align: center; font-size: large; padding-bottom: 0.3em;" | The CAA approved the new engine in October 1954 for commercial production and sale. This concept had been considered as early as 1945. Something went wrong. Among his many achievements was the development and creation of the ramjet-powered Hiller HJ-1/YH-32 Hornet. Fuel, as a gas or liquid vapour, is either mixed with the air in the intake or directly injected into the combustion chamber. As it was developed, the helicopter took on its own form of convention: Two rotors, a main lifting rotor and a tail anti-torque rotor, grew to be the norm. When Mike was asked by several bystanders if he were actually going to fly his ram-jet copter, Mike smiled and said, Yes eventually Well, Mike, we wish you the best of luck. This one is concerned with up and down flight or, if moved from side to side, operates the rudder to control the heading of the aircraft. It turns out that Mike purchased the plans for the craft from B.W. Eight years earlier, in the midst of the Second World War, Austrian engineer Friedrich von Doblhoff built and flew his WNF 342, which sent compressed air and fuel inside the rotor blades to combustion chambers on the blade tips for propulsion. The front of the cabin comprises two very large Plexiglas panels and their frames. Really neat piece of equipment and you can easily see how much simpler the total design was compared to other helicopter designs. [9] Technically the term for this engine is the acoustic-type pulsejet, or aerodynamically valved pulsejet. The second unit is a pressure jet which is usually propelled by fuel under pressure. Descriptive information to help identify this report. The pulse detonation engine (PDE) marks a new approach towards non-continuous jet engines and promises higher fuel efficiency compared to turbofan jet engines, at least at very high speeds. The improved updated HJ-1 Hornet was designated the H-32 for the Army, and HOE-1 for the Navy. The range dropped to only 28 miles (45 kilometers), while the endurance was reduced to about 30 minutes. The present international situation, however, has dictated that the resources of the Hiller factory be devoted entirely to Service production of the type 360. When the air-fuel is ignited, these valves slam shut which means that the hot gases can only leave through the engine's tailpipe, thus creating forward thrust. Over time, the military decided that the aircrafts short range, high fuel consumption, its potential for fuel starvation, and concerns with its autorotation capabilities would not meet the acceptance standards for both the Army and Navy. Mike reported that the motors are rated at 20 pounds of static thrust, and really spin the rotor up. |-. Will it fly? Other potential industry uses were for aerial photography, publicity, courier service, and for executive transportation. Civil Aeronautics Authority (CAA) commercial certification was underway by early 1951, with commercial marketing of the Hornet planned for the spring of 1951. The small tail rotor helped to improve yaw control in the performance of the H-32. Because pulsejets are an efficient and simple way to convert fuel into heat, experimenters are using them for new industrial applications such as biomass fuel conversion, boiler and heater systems, and other applications. By this time, the rotors are already spinning at a good rate, and the noise, as Mike admits, is a low roar similar to that put out by a roofers tar pot heating up. It consists of a two-seat enclosed cabin and a tail boom, both constructed from tubular steel and covered with plastic material. Most PDE research programs use pulsejet engines for testing ideas early in the design phase. This pressure is less than the inlet pressure (upstream of the one-way valve), and so the induction phase of the cycle begins. trzmiel jk helicopter pzl swidnik jet rotorcraft powered By properly 'tuning' the system (by designing the engine dimensions properly), a resonating combustion process can be achieved. The empty weight of the H-32 increased to 530 lb. It is by no means fantastic to foresee helicopter despatch-riders with machines rugged and simple enough to be maintained in an M.T. (110 km/h) with a top speed of 80 m.p.h. Schmidt's prototype bomb failed to meet German Air Ministry specifications, especially owing to poor accuracy, range and high cost. If youve been to any EAA Fly-In lately, youve undoubtedly seen many examples of Burt Rutans once-revolutionary designs, so you know this is true. With Schmidt now working for Argus, the pulsejet was perfected and was officially known by its RLM designation as the Argus As 109-014. Your email address will not be published.
An easy way to remember which is which is to repeat to yourself turbines turn, and jets jet. He was already thinking of using the technology on a larger scale, dreaming of a future when large heavy-lift flying cranes, and passenger carrying sky buses would fly using tip-powered jets. Instead, this copter had, on the ends of the rotors, what looked like small buzz bomb motors and, in back of the two seats, on the small frame, there were three five-gallon propane cylinders. (240 kg), with the gross weight now 1,080 lb. Steam power to fire the piston was generated by the violent exothermic chemical reaction created when hydrogen peroxide and potassium permanganate (termed T-Stoff and Z-Stoff) are combined. It has been viewed 266 times. A 25-lb. Your email address will not be published. The department is a member of the FDLP Content Partnerships Program and an Affiliated Archive of the National Archives. The helicopter was reportedly very stable due to the proven Hiller Rotor-Matic paddles and the aircrafts high-inertia rotor. report UNT Libraries Government Documents Department, National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics. In 1909, Georges Marconnet developed the first pulsating combustor without valves. jet rc engine planes radio drone control pulsejet aircraft engines pulse The military had requested the changes to make the aircrafts controls common with other helicopters in its fleet. While the thrust-to-weight ratio is excellent, thrust specific fuel consumption is generally very poor. Remember, as with Wikipedia, it only takes a few dollars once from every person who visits to cover our running costs. All told, Hiller manufactured 25 Hornets, and about half have survived, on display in museums across the U.S. and in private collections. The ramjet engine was also updated with a larger diameter, and new weight of 12.7 lb. Ignition in the As 014 was provided by a single automotive spark plug, mounted approximately 75cm (30in) behind the front-mounted valve array. This selection of materials from the Technical Report Archive and Image Library (TRAIL) includes hard-to-find reports published by various government agencies. This website is 100% self funded, and has been since 2006. Add to cart to save with this special offer. Each unit developed 31 lb. An extensive test and development programme is in mind for them. The radical designs, however, caution is thrown to the winds in the quest to prove an idea, and looks be dammed. Starting with ignition within the combustion chamber, a high pressure is raised by the combustion of the fuel-air mixture. The technical publications contain reports, images, and technical descriptions of research performed for U.S. government agencies. UNT Digital Library, Hillers engineers evaluated turbojet, pulsejet, and ramjet engines, and tested them extensively on a whirl stand and a static test stand. While some valveless engines are known for being extremely fuel-hungry, other designs use significantly less fuel than a valved pulsejet, and a properly designed system with advanced components and techniques can rival or exceed the fuel efficiency of small turbojet engines. Radin, Edward J. The French inventor Georges Marconnet patented his valveless pulsejet engine in 1908, which many commentators argue[attribution needed] greatly influenced the V-1 flying bomb through engineer Paul Schmidt, who pioneered a more efficient design based on modification of the intake valves (or flaps), earning him government support from the German Air Ministry in 1933. The cycle frequency is primarily dependent on the length of the engine. However, because there is no fly-wheel effect with a pulse jet, any minor interruption of the fuel flow can cause a flame-out. University of North Texas Libraries, UNT Digital Library, National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics Collection, 25 The helicopter was once a very radical design too. Even with the end of the Hornet program, Hiller had not given up on the promise of tip-jet propulsion. In 1934, Georg Madelung and Munich-based independent designer and inventor Paul Schmidt proposed to the German Air Ministry a "flying bomb" powered by Schmidt's pulse jet. The ramjets, which have no moving parts, are constructed from heat-resisting steel, and they are attached to the blade tips by two bolts and a steel support. Pulsejet engines can be made with few[1] or no moving parts,[2][3][4] and are capable of running statically. The second type of pulsejet is known as the valveless pulsejet. This causes atomized fuel at the rear of the combustion chamber to "flash" as it comes in contact with the hot gases of the preceding column of gasthis resulting flash "slams" the reed-valves shut or in the case of valveless designs, stops the flow of fuel until a vacuum is formed and the cycle repeats. Seller assumes all responsibility for this listing. The three propane cylinders feed into a control manifold and an All valve which controls the flow of liquid propane to the motors. This used a fan blower, placed underneath the engine, which could be directed to counter torque. With commercial certification on hold, Hiller gauged the militarys interest in the Hornet. Most experienced modelers are familiar with another famous pulse jet the Dynajet which holds many speed records for model aircraft. Pulsejet fuel efficiency is a topic for hot debate, as efficiency is a relative term. One company, Beck Technologies, has produced a valved pulsejet design with variable intake geometry, allowing the intake to open and close to control ram airflow, and letting the engine produce full power at any speed. The valveless pulsejet was experimented with by the French propulsion research group SNECMA (Socit Nationale d'tude et de Construction de Moteurs d'Aviation ), in the late 1940s. The simplicity of the new Hiller-Hornet was described in a 1951 special edition of the Hiller Copter-News. Pulsejet engines are characterized by simplicity, low cost of construction, and high noise levels. start to build-up rapidly. The ceiling at full gross load was 12,000 feet (3,650 meters). Hiller decided to give up on marketing the Hornet commercially after the CAA did not approve civil certification. Hiller had long been fascinated by the idea of finding new ways to perform vertical flight that eliminated the need for a tail rotor. plane debunked smokers metabunk experimenter eaa mystery articles Evaluations by the U.S. military would also prove the claims of lower cost and maintenance for this type of helicopter. At the operational rotor speed of 500 r.p.m. They can achieve higher top speeds, with some advanced designs being capable of operating at Mach .7 or possibly higher. All production of Hillers helicopters was focused on the military. For a small model-type engine the frequency may be around 250 pulses per second, whereas for a larger engine such as the one used on the German V-1 flying bomb, the frequency was closer to 45 pulses per second. The rotor may be hand-cranked, or turned by a portable electric motor with battery, or rotated by a small two-stroke petrol engine (described as of the motor-mower type but better explained, perhaps, as an inboard outboard built into the aircraft. He built and flew the first coaxial helicopter (the XH-44) in the U.S. in 1944, when he was just 19. Autorotation on a Hornet kept the experienced pilot honest. colspan="2" style="text-align: center; font-size: large; padding-bottom: 0.3em;" | The CAA approved the new engine in October 1954 for commercial production and sale. This concept had been considered as early as 1945. Something went wrong. Among his many achievements was the development and creation of the ramjet-powered Hiller HJ-1/YH-32 Hornet. Fuel, as a gas or liquid vapour, is either mixed with the air in the intake or directly injected into the combustion chamber. As it was developed, the helicopter took on its own form of convention: Two rotors, a main lifting rotor and a tail anti-torque rotor, grew to be the norm. When Mike was asked by several bystanders if he were actually going to fly his ram-jet copter, Mike smiled and said, Yes eventually Well, Mike, we wish you the best of luck. This one is concerned with up and down flight or, if moved from side to side, operates the rudder to control the heading of the aircraft. It turns out that Mike purchased the plans for the craft from B.W. Eight years earlier, in the midst of the Second World War, Austrian engineer Friedrich von Doblhoff built and flew his WNF 342, which sent compressed air and fuel inside the rotor blades to combustion chambers on the blade tips for propulsion. The front of the cabin comprises two very large Plexiglas panels and their frames. Really neat piece of equipment and you can easily see how much simpler the total design was compared to other helicopter designs. [9] Technically the term for this engine is the acoustic-type pulsejet, or aerodynamically valved pulsejet. The second unit is a pressure jet which is usually propelled by fuel under pressure. Descriptive information to help identify this report. The pulse detonation engine (PDE) marks a new approach towards non-continuous jet engines and promises higher fuel efficiency compared to turbofan jet engines, at least at very high speeds. The improved updated HJ-1 Hornet was designated the H-32 for the Army, and HOE-1 for the Navy. The range dropped to only 28 miles (45 kilometers), while the endurance was reduced to about 30 minutes. The present international situation, however, has dictated that the resources of the Hiller factory be devoted entirely to Service production of the type 360. When the air-fuel is ignited, these valves slam shut which means that the hot gases can only leave through the engine's tailpipe, thus creating forward thrust. Over time, the military decided that the aircrafts short range, high fuel consumption, its potential for fuel starvation, and concerns with its autorotation capabilities would not meet the acceptance standards for both the Army and Navy. Mike reported that the motors are rated at 20 pounds of static thrust, and really spin the rotor up. |-. Will it fly? Other potential industry uses were for aerial photography, publicity, courier service, and for executive transportation. Civil Aeronautics Authority (CAA) commercial certification was underway by early 1951, with commercial marketing of the Hornet planned for the spring of 1951. The small tail rotor helped to improve yaw control in the performance of the H-32. Because pulsejets are an efficient and simple way to convert fuel into heat, experimenters are using them for new industrial applications such as biomass fuel conversion, boiler and heater systems, and other applications. By this time, the rotors are already spinning at a good rate, and the noise, as Mike admits, is a low roar similar to that put out by a roofers tar pot heating up. It consists of a two-seat enclosed cabin and a tail boom, both constructed from tubular steel and covered with plastic material. Most PDE research programs use pulsejet engines for testing ideas early in the design phase. This pressure is less than the inlet pressure (upstream of the one-way valve), and so the induction phase of the cycle begins. trzmiel jk helicopter pzl swidnik jet rotorcraft powered By properly 'tuning' the system (by designing the engine dimensions properly), a resonating combustion process can be achieved. The empty weight of the H-32 increased to 530 lb. It is by no means fantastic to foresee helicopter despatch-riders with machines rugged and simple enough to be maintained in an M.T. (110 km/h) with a top speed of 80 m.p.h. Schmidt's prototype bomb failed to meet German Air Ministry specifications, especially owing to poor accuracy, range and high cost. If youve been to any EAA Fly-In lately, youve undoubtedly seen many examples of Burt Rutans once-revolutionary designs, so you know this is true. With Schmidt now working for Argus, the pulsejet was perfected and was officially known by its RLM designation as the Argus As 109-014. Your email address will not be published.  The first working pulsejet was patented in 1906 by Russian engineer V.V. The daisy valve is less effective than a rectangular valve grid, although it is easier to construct on a small scale. Incidental advantages claimed for the Hornets ramjet power source are best listed as negatives: no carburetor to ice up; no ignition system to fail or require maintenance; no radio interference; no warming-up delays; and practically no general maintenance. Designers of modern cruise missiles do not choose pulsejet engines for propulsion, preferring turbojets or rocket engines. [6] Pulsejets have also been used in both control-line and radio-controlled model aircraft. General Henry Harley "Hap" Arnold of the United States Army Air Forces was concerned that this weapon could be built of steel and wood, in 2000 man hours and approximate cost of US$600 (in 1943).[5]. Ram jets are very fuel hungry. Hiller was not impressed with the reduced performance caused by the militarys changes. The Army followed up with another order for 12 H-32s, for a total of 14. Either a fuel pump or propane is usually used. That flight was piloted by Hiller chief test pilot Frank Peterson, but test pilot Bruce Jones did most of the experimental flight testing on the aircraft. One notable line of research of pulsejet engines includes the pulse detonation engine which involves repeated detonations in the engine, and which can potentially give high compression and good efficiency. The valves prevent the explosive gas of the ignited fuel mixture in the combustion chamber from exiting and disrupting the intake airflow, although with all practical valved pulsejets there is some 'blowback' while running statically and at low speed as the valves cannot close fast enough to stop all the gas from exiting the intake. With no torque to counter due to the lack of a traditional engine and transmission system that would normally generate it, there was no need for a tail rotor. We appreciate your consideration in this matter. In addition to the control levers the cabin contains a wobble pump, a starting button, a fuel-flow gauge, a rotor r.p.m. The small, utility two-place helicopter weighed 356 lb. The basic hovering characteristics of the rotor and propulsive characteristics of the pulse-jet engine were obtained at a range of engine speeds with the engines rigidly fixed to the blade tips and with the engines free to pivot. The National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) was a U.S. federal agency founded on March 3, 1915 to undertake, promote, and institutionalize aeronautical research. The two-bladed all-metal rotor system attached to a teetering type rotor hub. The U.S. Army and U.S. Navy ordered an evaluation quantity of the two-place upgraded Hornet in June 1952. This limits the maximum (pre-combustion) pressure ratio, to perhaps 1.2 to 1.
The first working pulsejet was patented in 1906 by Russian engineer V.V. The daisy valve is less effective than a rectangular valve grid, although it is easier to construct on a small scale. Incidental advantages claimed for the Hornets ramjet power source are best listed as negatives: no carburetor to ice up; no ignition system to fail or require maintenance; no radio interference; no warming-up delays; and practically no general maintenance. Designers of modern cruise missiles do not choose pulsejet engines for propulsion, preferring turbojets or rocket engines. [6] Pulsejets have also been used in both control-line and radio-controlled model aircraft. General Henry Harley "Hap" Arnold of the United States Army Air Forces was concerned that this weapon could be built of steel and wood, in 2000 man hours and approximate cost of US$600 (in 1943).[5]. Ram jets are very fuel hungry. Hiller was not impressed with the reduced performance caused by the militarys changes. The Army followed up with another order for 12 H-32s, for a total of 14. Either a fuel pump or propane is usually used. That flight was piloted by Hiller chief test pilot Frank Peterson, but test pilot Bruce Jones did most of the experimental flight testing on the aircraft. One notable line of research of pulsejet engines includes the pulse detonation engine which involves repeated detonations in the engine, and which can potentially give high compression and good efficiency. The valves prevent the explosive gas of the ignited fuel mixture in the combustion chamber from exiting and disrupting the intake airflow, although with all practical valved pulsejets there is some 'blowback' while running statically and at low speed as the valves cannot close fast enough to stop all the gas from exiting the intake. With no torque to counter due to the lack of a traditional engine and transmission system that would normally generate it, there was no need for a tail rotor. We appreciate your consideration in this matter. In addition to the control levers the cabin contains a wobble pump, a starting button, a fuel-flow gauge, a rotor r.p.m. The small, utility two-place helicopter weighed 356 lb. The basic hovering characteristics of the rotor and propulsive characteristics of the pulse-jet engine were obtained at a range of engine speeds with the engines rigidly fixed to the blade tips and with the engines free to pivot. The National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) was a U.S. federal agency founded on March 3, 1915 to undertake, promote, and institutionalize aeronautical research. The two-bladed all-metal rotor system attached to a teetering type rotor hub. The U.S. Army and U.S. Navy ordered an evaluation quantity of the two-place upgraded Hornet in June 1952. This limits the maximum (pre-combustion) pressure ratio, to perhaps 1.2 to 1.  When the induction phase is under way, fuel in atomized form is injected into the combustion chamber to fill the vacuum formed by the departing of the previous fireball; the atomized fuel tries to fill up the entire tube including the tailpipe. The high noise levels usually make them impractical for other than military and other similarly restricted applications. Pulsejet engines, being cheap and easy to construct, were the obvious choice for the V-1's designers, given the Germans' materials shortages and overstretched industry at that stage of the war. Three YH-32A helicopters were manufactured and evaluated at the Fort Rucker Army facility in Alabama during 1957. The last of these jets is the ram jet which gets its power from gasses being introduced into the combustion chamber while the ram jet is in motion, thus the name. Getting going in the Hornet was quite simple. The H-32 became the Armys first operational ramjet helicopter, and the HOE-1 was the Navys first tip-powered jet helicopter. [6] However, pulsejets are used on a large scale as industrial drying systems, and there has been a new surge to study and apply these engines to applications such as high-output heating, biomass conversion, and alternative energy systems, as pulsejets can run on almost anything that burns, including particulate fuels such as sawdust or coal powder. The company soon had three prototypes flying: the original streamlined fiberglass-enclosed two-seater, and two stripped-down utility versions. piston engine, but that when the machine is hovering it is somewhat louder.
When the induction phase is under way, fuel in atomized form is injected into the combustion chamber to fill the vacuum formed by the departing of the previous fireball; the atomized fuel tries to fill up the entire tube including the tailpipe. The high noise levels usually make them impractical for other than military and other similarly restricted applications. Pulsejet engines, being cheap and easy to construct, were the obvious choice for the V-1's designers, given the Germans' materials shortages and overstretched industry at that stage of the war. Three YH-32A helicopters were manufactured and evaluated at the Fort Rucker Army facility in Alabama during 1957. The last of these jets is the ram jet which gets its power from gasses being introduced into the combustion chamber while the ram jet is in motion, thus the name. Getting going in the Hornet was quite simple. The H-32 became the Armys first operational ramjet helicopter, and the HOE-1 was the Navys first tip-powered jet helicopter. [6] However, pulsejets are used on a large scale as industrial drying systems, and there has been a new surge to study and apply these engines to applications such as high-output heating, biomass conversion, and alternative energy systems, as pulsejets can run on almost anything that burns, including particulate fuels such as sawdust or coal powder. The company soon had three prototypes flying: the original streamlined fiberglass-enclosed two-seater, and two stripped-down utility versions. piston engine, but that when the machine is hovering it is somewhat louder.